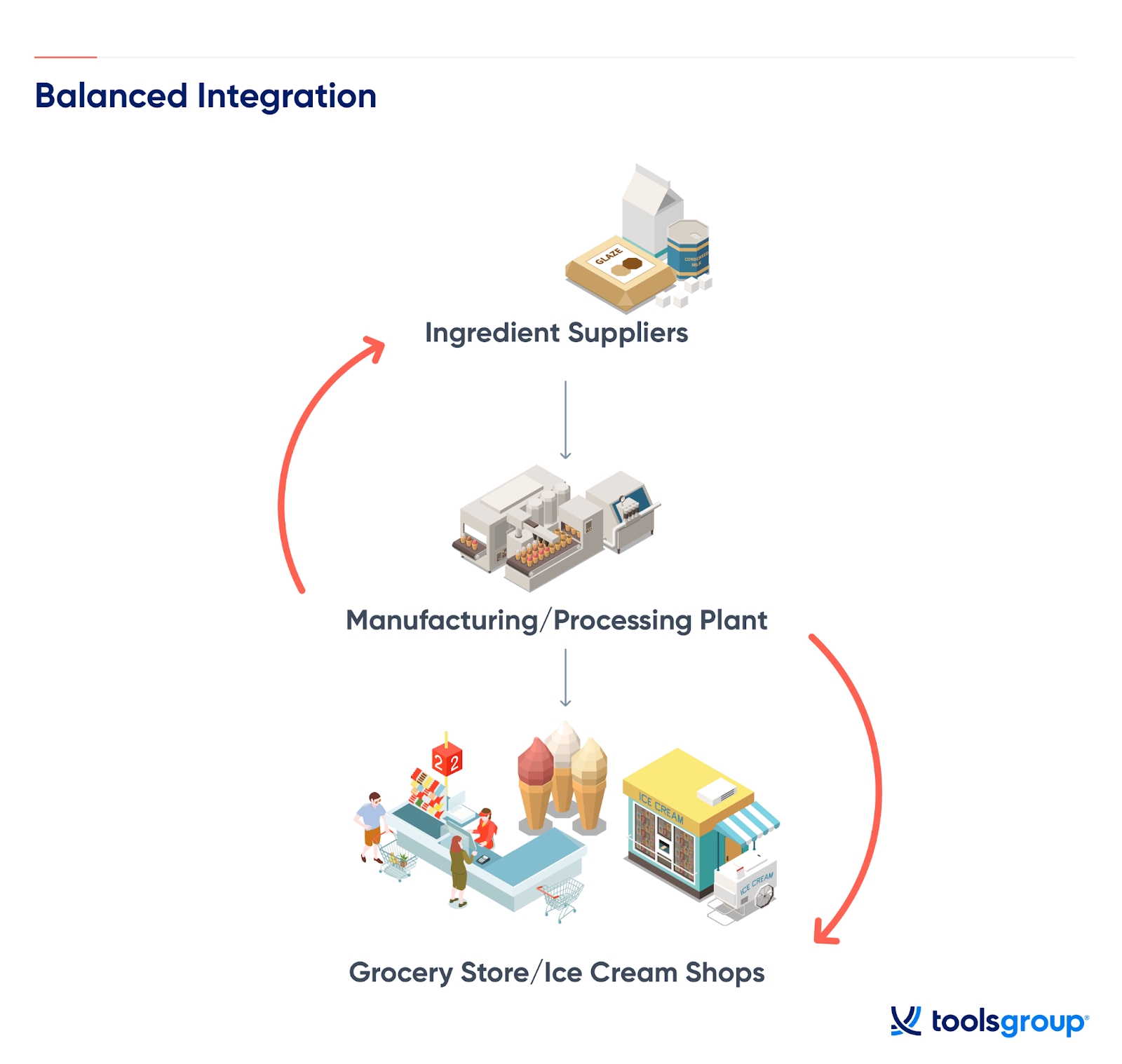
Vertical integration APUSH is not just a term you stumble upon in your history books; it's a concept that shaped the backbone of American industrialization. Imagine a time when businesses weren’t just competing but were redefining the rules of the game. Vertical integration became a game-changer, allowing companies to control every aspect of production from raw materials to the finished product. This gave them an edge over competitors and revolutionized industries like steel and oil.
Now, before we dive headfirst into this historical journey, let’s set the stage. Picture yourself in the late 19th century, where the industrial revolution was in full swing. Businesses were booming, and entrepreneurs were looking for ways to maximize profits while minimizing costs. Enter vertical integration—a strategy that allowed companies to own and operate every stage of production, eliminating the need for third-party suppliers.
This article isn’t just about definitions; it’s about understanding how vertical integration played a pivotal role in shaping the American economy. We’ll explore its origins, its impact on key industries, and why it remains a critical concept in the APUSH (Advanced Placement United States History) curriculum. So, buckle up, and let’s get started!
What Exactly is Vertical Integration?
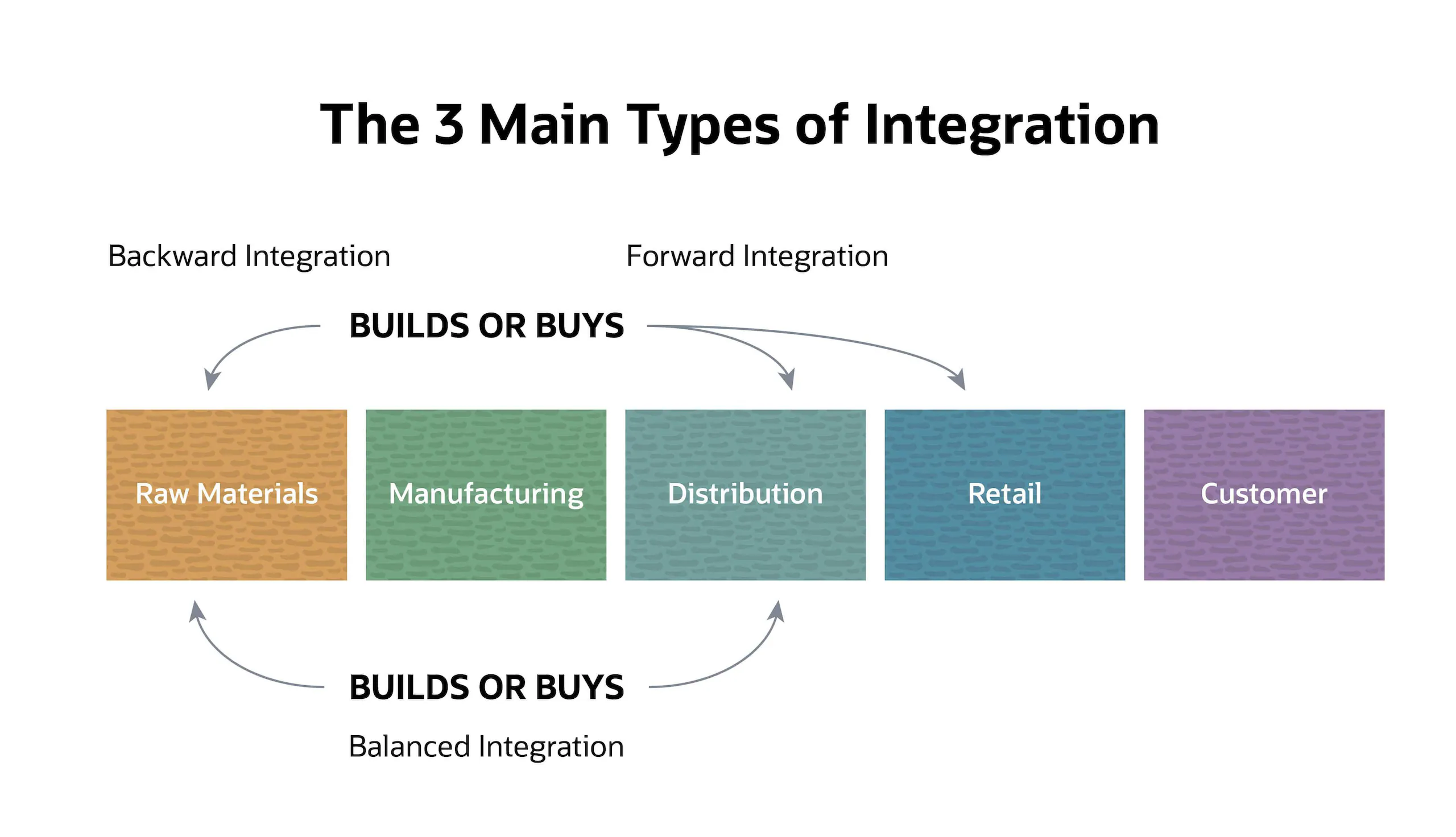
Let’s break it down. Vertical integration is all about control—control over the entire production process. Think of it as a company owning everything from the source of raw materials to the final product that hits the shelves. This strategy can be divided into two types: backward and forward integration. Backward integration involves controlling the supply chain, while forward integration focuses on distribution and retail.
In the context of APUSH, vertical integration was a tool used by industrial giants like Andrew Carnegie and John D. Rockefeller to dominate their respective industries. By controlling every step of the process, they were able to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and increase profits. This wasn’t just about making more money; it was about creating a monopoly-like structure that stifled competition.
The Origins of Vertical Integration
To truly understand vertical integration, we need to go back to its roots. The concept gained traction during the late 1800s, a period marked by rapid industrialization and innovation. Companies realized that by owning the means of production, they could streamline operations and eliminate middlemen. This was a revolutionary idea at the time, and it quickly became a popular strategy among entrepreneurs.
Key Players in the Game
When it comes to vertical integration, two names stand out: Andrew Carnegie and John D. Rockefeller. Carnegie revolutionized the steel industry by controlling everything from iron ore mines to steel mills. Similarly, Rockefeller’s Standard Oil became a powerhouse by owning oil wells, refineries, and even transportation networks. These men weren’t just businessmen; they were visionaries who understood the power of control.
Vertical Integration in Action: The Steel Industry
Let’s take a closer look at how vertical integration transformed the steel industry. Andrew Carnegie didn’t just build steel mills; he controlled the entire supply chain. From owning the iron ore mines to building his own railroads, Carnegie eliminated the need for third-party suppliers. This allowed him to produce steel at a fraction of the cost, making him one of the richest men in history.
Here’s a quick breakdown of Carnegie’s approach:
- Controlled iron ore mines to secure raw materials.
- Built his own railroads to transport goods.
- Owned the steel mills where production took place.
This level of control gave Carnegie a significant advantage over his competitors, allowing him to undercut prices and dominate the market.
Vertical Integration in the Oil Industry
John D. Rockefeller’s Standard Oil is another prime example of vertical integration in action. Rockefeller didn’t just drill for oil; he controlled every aspect of the oil industry. From owning oil wells to building refineries and transportation networks, Rockefeller created a monopoly that controlled nearly 90% of the oil production in the United States.
The Impact of Standard Oil
The impact of Standard Oil on the American economy was profound. By controlling the entire production process, Rockefeller was able to drive down costs and increase efficiency. However, this also led to concerns about monopolistic practices, ultimately resulting in the breakup of Standard Oil in 1911. This case highlighted the double-edged sword of vertical integration—while it brought efficiency, it also raised questions about fairness and competition.
Benefits of Vertical Integration
So, why did companies choose vertical integration? The benefits are clear:
- Cost reduction: By eliminating middlemen, companies could significantly reduce costs.
- Improved efficiency: Controlling every stage of production allowed for better coordination and reduced downtime.
- Increased profits: With lower costs and improved efficiency, companies could increase their profit margins.
These benefits made vertical integration an attractive option for businesses looking to gain a competitive edge. However, as we’ll see, there were also drawbacks to this strategy.
Challenges and Criticisms of Vertical Integration
While vertical integration brought many advantages, it wasn’t without its challenges. One of the biggest criticisms was the potential for monopolistic practices. By controlling every aspect of production, companies could stifle competition and create barriers to entry for smaller businesses. This led to increased scrutiny from government regulators and eventually resulted in antitrust laws.
The Role of Antitrust Laws
The Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890 was one of the first laws aimed at curbing monopolistic practices. This law made it illegal for companies to engage in activities that restrained trade or commerce. The breakup of Standard Oil in 1911 was a direct result of this legislation, highlighting the need for regulatory oversight in the business world.
Vertical Integration in Modern Times
Fast forward to today, and vertical integration is still a relevant strategy in the business world. Companies like Amazon and Tesla are using this approach to gain a competitive edge in their respective industries. By controlling everything from production to distribution, these companies are able to offer innovative products at competitive prices.
However, the challenges remain the same. As companies grow larger, there’s always the risk of monopolistic practices and regulatory scrutiny. This raises important questions about the balance between efficiency and fairness in the business world.
Why Vertical Integration Matters in APUSH
Vertical integration is a critical concept in the APUSH curriculum because it helps students understand the economic and social changes that occurred during the industrial revolution. By studying how companies like Carnegie Steel and Standard Oil used vertical integration to dominate their industries, students gain insight into the forces that shaped the American economy.
Key Takeaways for Students
Here are a few key takeaways for APUSH students:
- Vertical integration was a strategy used by industrial giants to control every aspect of production.
- This strategy led to increased efficiency and reduced costs but also raised concerns about monopolistic practices.
- The Sherman Antitrust Act was one of the first laws aimed at curbing monopolies and promoting fair competition.
Understanding these concepts is essential for anyone studying American history, as they provide a window into the economic forces that shaped the nation.
Conclusion
Vertical integration APUSH is more than just a term; it’s a concept that continues to influence the business world today. By understanding its origins, impact, and challenges, we gain a deeper appreciation for the forces that shaped the American economy. Whether you’re a student studying APUSH or a business professional looking to gain a competitive edge, vertical integration is a topic worth exploring.
So, what’s next? If you found this article helpful, feel free to share it with your friends or leave a comment below. And if you’re looking for more insights into American history, be sure to check out our other articles. History isn’t just about the past; it’s about understanding the present and shaping the future.
Table of Contents
- What Exactly is Vertical Integration?
- The Origins of Vertical Integration
- Key Players in the Game
- Vertical Integration in Action: The Steel Industry
- Vertical Integration in the Oil Industry
- Benefits of Vertical Integration
- Challenges and Criticisms of Vertical Integration
- Vertical Integration in Modern Times
- Why Vertical Integration Matters in APUSH
- Conclusion